Graphic
Marine cloud brightening
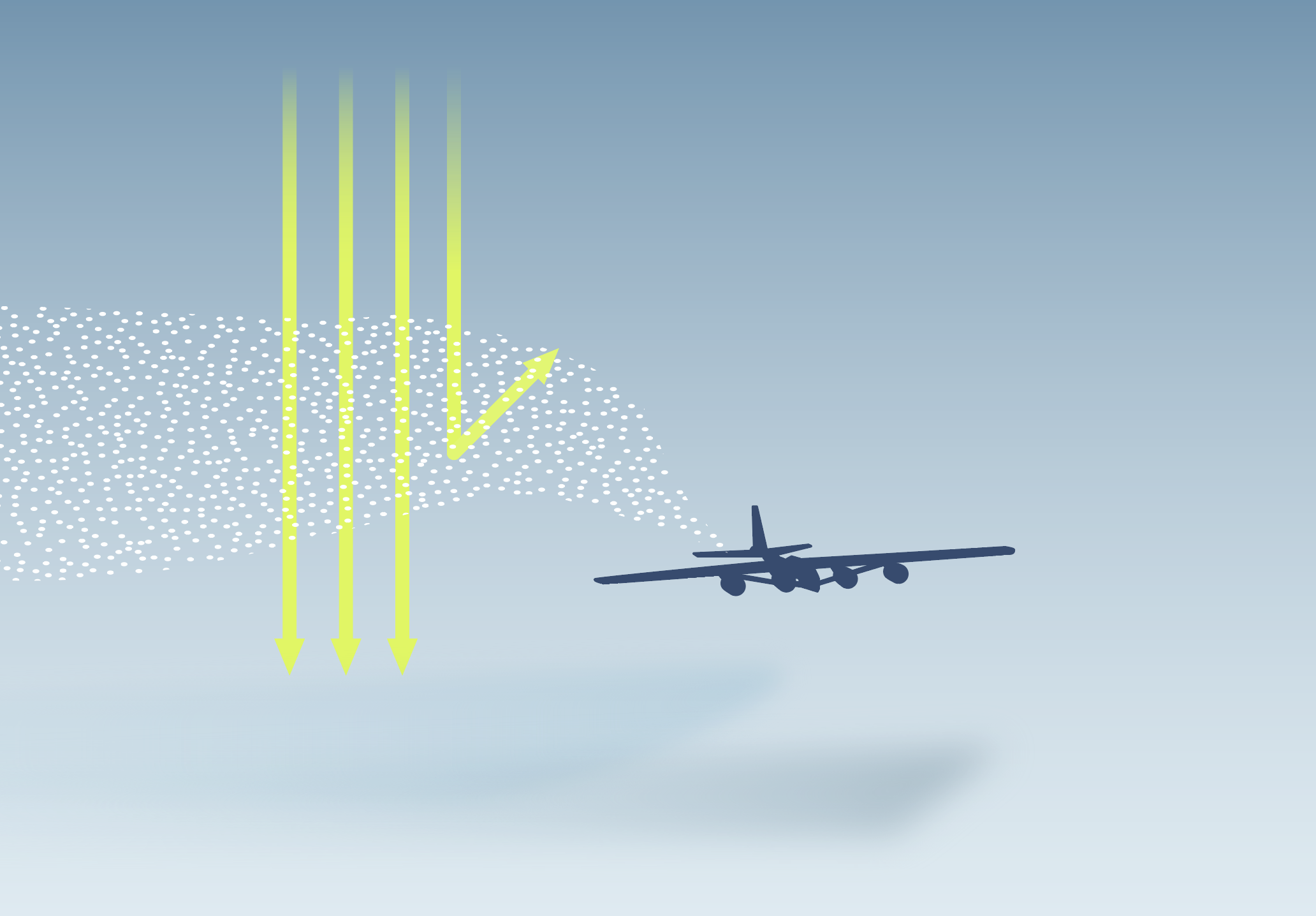
Marine cloud brightening (MCB) is an idea to enhance the reflectivity of low-lying clouds over the oceans. MCB may be able to produce a large regional cooling effect, but the uneven cooling may lead to large shifts in global rainfall patterns.
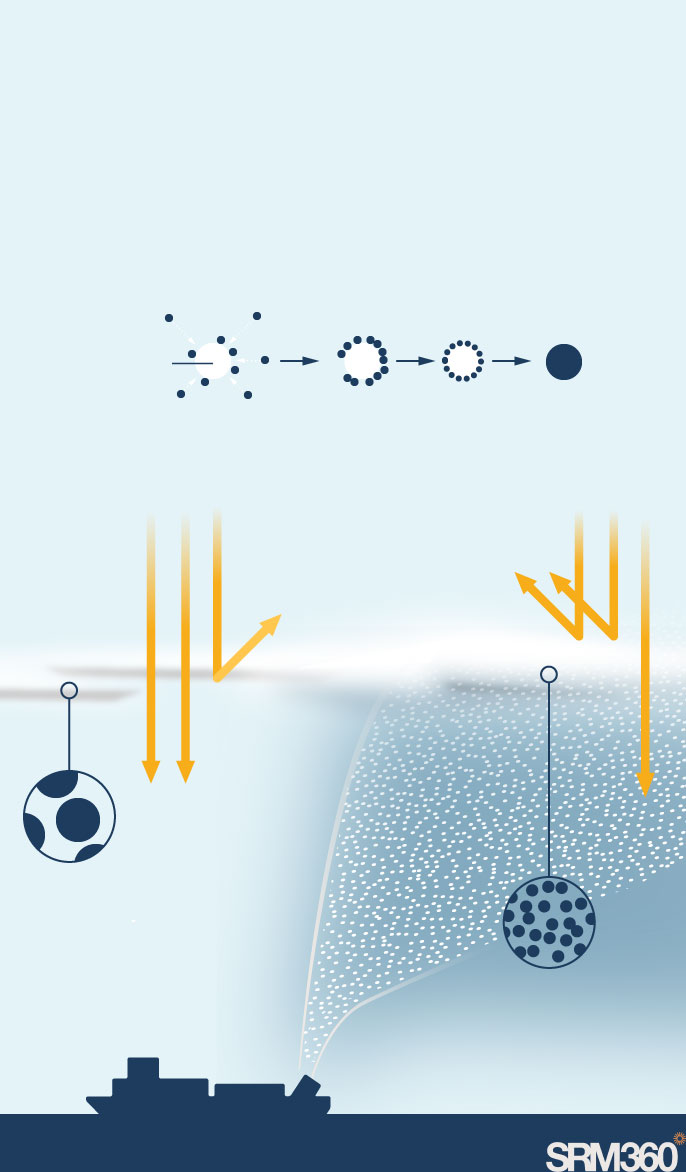
Ships would spray tiny sea salt particles into the clouds. These particles are so small they stay suspended in the air and act as seeds for forming new, smaller cloud droplets.
Water molecules condense around the particle to form a cloud droplet
Sea-salt particle
Droplet
Water molecule
Clouds with fewer, larger cloud droplets reflect less light
More, smaller droplets reflect more light.
Source: SRM360.org
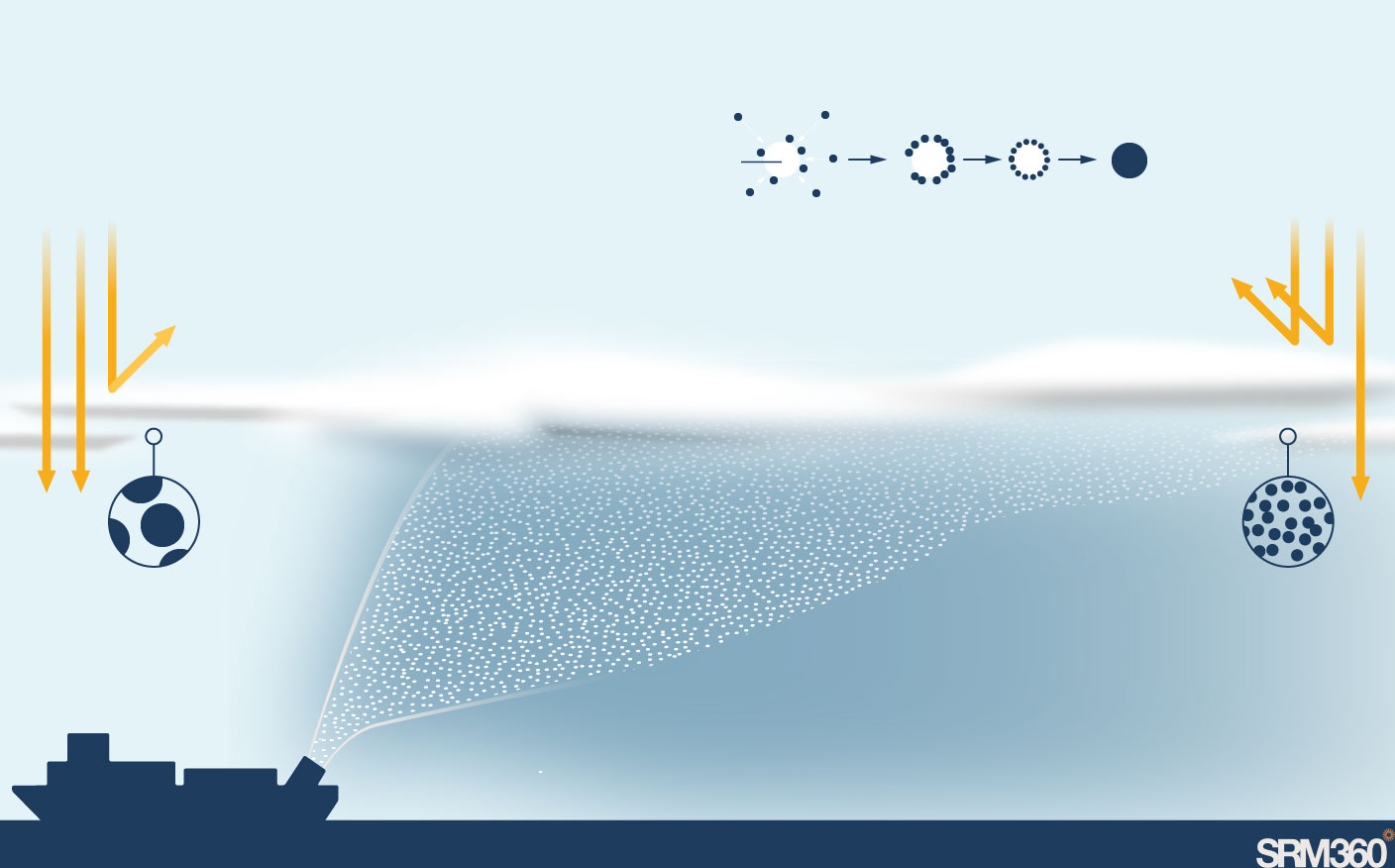
Ships would spray tiny sea salt particles into the clouds. These particles are so small they stay suspended in the air and act as seeds for forming new, smaller cloud droplets.
Water molecules condense around the particle to form a cloud droplet
Sea-salt particle
Droplet
Water molecule
More, smaller droplets reflect more light.
Clouds with fewer, larger cloud droplets reflect less light
Source: SRM360.org
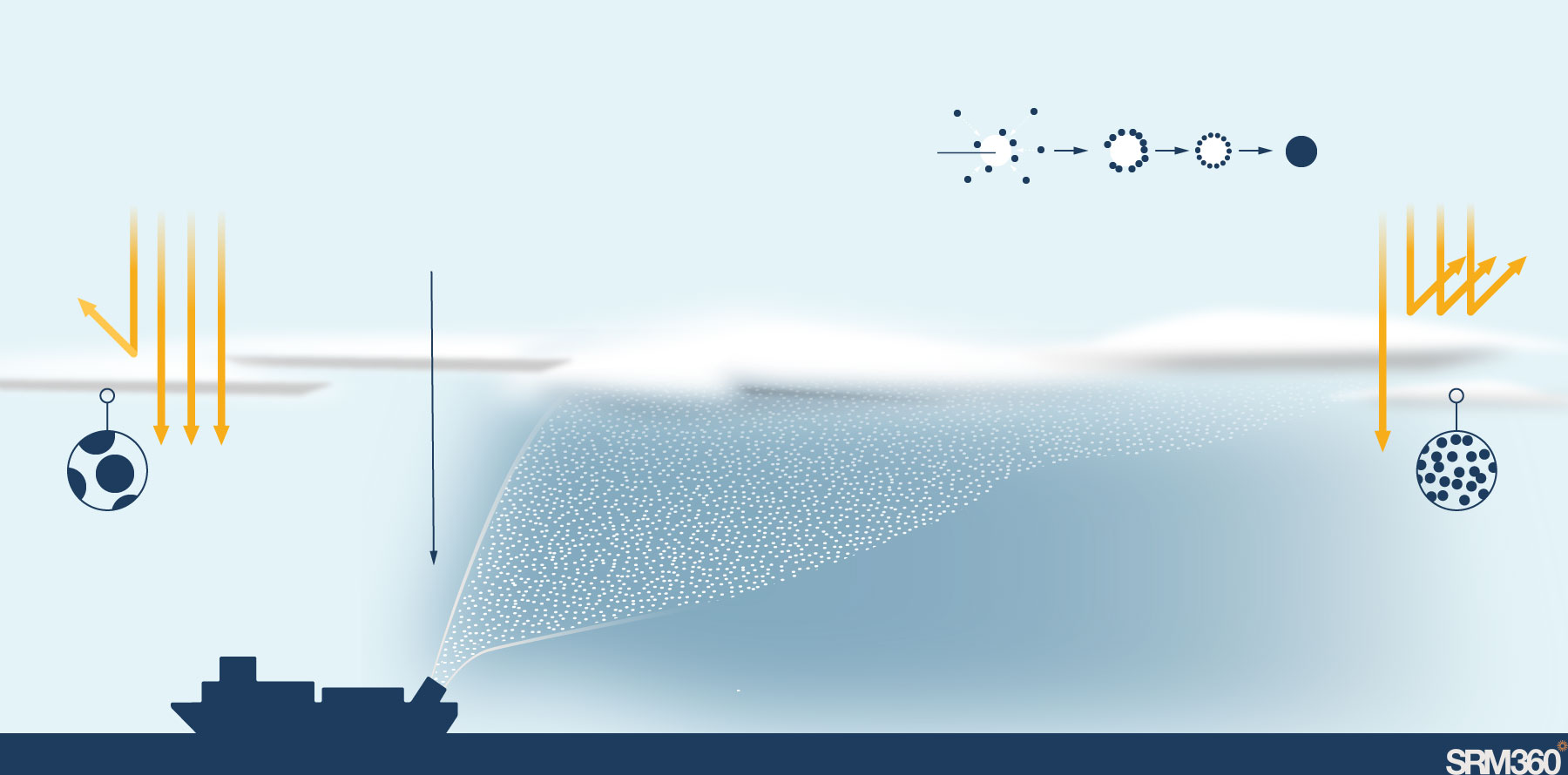
Ships would spray tiny sea salt particles into the clouds. These particles are so small they stay suspended in the air and act as seeds for forming new, smaller cloud droplets.
Water molecules condense around the particle to form a cloud droplet
Sea-salt particle
Droplet
Water molecule
Clouds with fewer, larger cloud droplets reflect less light
More, smaller droplets reflect more light.
Source: SRM360.org